虚拟列:JSON 数据自动加速
VIRTUAL COLUMN是企业版功能。 如需获取许可证,请联系 Databend 支持团队。
虚拟列自动加速存储在 VARIANT 列中的半结构化数据查询,为 JSON 数据访问提供零配置性能优化。
解决了什么问题?
查询 JSON 数据时,传统数据库每次访问嵌套字段都需解析整个 JSON 结构,导致性能瓶颈:
| 问题 | 影响 | 虚拟列解决方案 |
|---|---|---|
| 查询延迟 | 复杂 JSON 查询耗时数秒 | 亚秒级响应时间 |
| 数据读取过多 | 即使只需单个字段也读取整个文档 | 仅读取所需字段 |
| JSON 解析缓慢 | 每次查询都重新解析完整文档 | 预物化字段实现即时访问 |
| CPU 使用率高 | JSON 遍历消耗大量算力 | 像常规数据直接读取 |
| 内存开销大 | 加载完整 JSON 结构到内存 | 仅加载必要字段 |
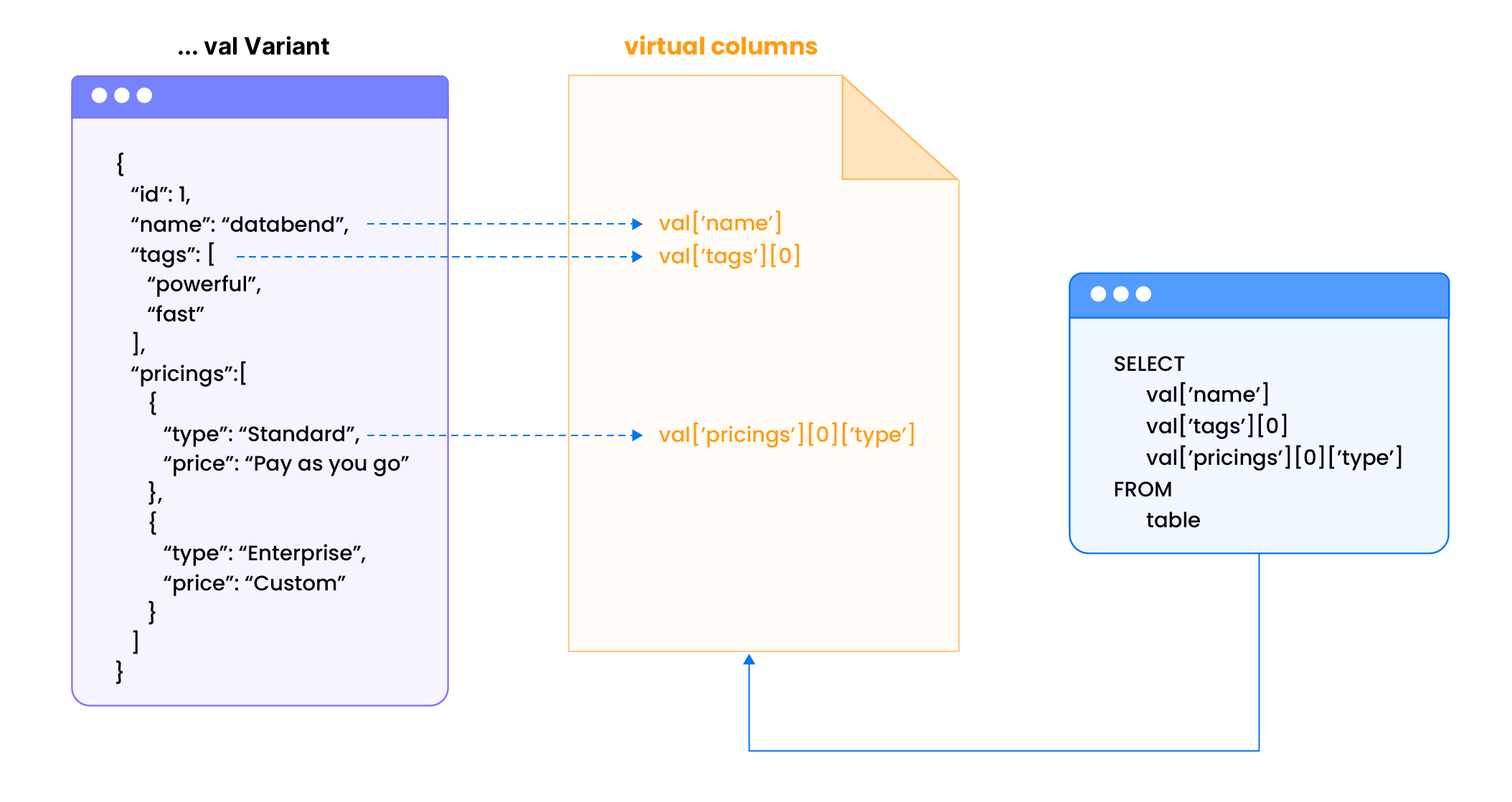
示例场景:电商分析表存储 JSON 格式产品数据。无虚拟列时,查询数百万行的 product_data['category'] 需解析每个 JSON 文档;使用虚拟列后变为直接列查找。
工作原理
- 数据摄取 → Databend 分析 VARIANT 列中的 JSON 结构
- 智能检测 → 识别高频访问的嵌套字段
- 后台优化 → 自动创建虚拟列
- 查询加速 → 自动使用优化路径
配置
虚拟列自 v1.2.832 起默认启用,无需额外配置。
完整示例
演示自动虚拟列创建与性能优势:
-- 创建表 'test',含整型 id 列和 Variant 类型 val 列
CREATE TABLE test(id int, val variant);
-- 插入含 Variant 数据的示例记录
INSERT INTO
test
VALUES
(
1,
'{"id":1,"name":"databend","tags":["powerful","fast"],"pricings":[{"type":"Standard","price":"Pay as you go"},{"type":"Enterprise","price":"Custom"}]}'
),
(
2,
'{"id":2,"name":"databricks","tags":["scalable","flexible"],"pricings":[{"type":"Free","price":"Trial"},{"type":"Premium","price":"Subscription"}]}'
),
(
3,
'{"id":3,"name":"snowflake","tags":["cloud-native","secure"],"pricings":[{"type":"Basic","price":"Pay per second"},{"type":"Enterprise","price":"Annual"}]}'
),
(
4,
'{"id":4,"name":"redshift","tags":["reliable","scalable"],"pricings":[{"type":"On-Demand","price":"Pay per usage"},{"type":"Reserved","price":"1 year contract"}]}'
),
(
5,
'{"id":5,"name":"bigquery","tags":["innovative","cost-efficient"],"pricings":[{"type":"Flat Rate","price":"Monthly"},{"type":"Flex","price":"Per query"}]}'
);
INSERT INTO test SELECT * FROM test;
INSERT INTO test SELECT * FROM test;
INSERT INTO test SELECT * FROM test;
INSERT INTO test SELECT * FROM test;
INSERT INTO test SELECT * FROM test;
-- 解释查询特定字段的执行计划
EXPLAIN
SELECT
val ['name'],
val ['tags'] [0],
val ['pricings'] [0] ['type']
FROM
test;
-[ EXPLAIN ]-----------------------------------
Exchange
├── output columns: [test.val['name'] (#3), test.val['pricings'][0]['type'] (#5), test.val['tags'][0] (#8)]
├── exchange type: Merge
└── TableScan
├── table: default.default.test
├── output columns: [val['name'] (#3), val['pricings'][0]['type'] (#5), val['tags'][0] (#8)]
├── read rows: 160
├── read size: 1.69 KiB
├── partitions total: 6
├── partitions scanned: 6
├── pruning stats: [segments: <range pruning: 6 to 6>, blocks: <range pruning: 6 to 6>]
├── push downs: [filters: [], limit: NONE]
├── virtual columns: [val['name'], val['pricings'][0]['type'], val['tags'][0]]
└── estimated rows: 160.00
-- 解释仅查询 name 字段的执行计划
EXPLAIN
SELECT
val ['name']
FROM
test;
-[ EXPLAIN ]-----------------------------------
Exchange
├── output columns: [test.val['name'] (#2)]
├── exchange type: Merge
└── TableScan
├── table: default.book_db.test
├── output columns: [val['name'] (#2)]
├── read rows: 160
├── read size: < 1 KiB
├── partitions total: 16
├── partitions scanned: 16
├── pruning stats: [segments: <range pruning: 6 to 6>, blocks: <range pruning: 16 to 16>]
├── push downs: [filters: [], limit: NONE]
├── virtual columns: [val['name']]
└── estimated rows: 160.00
-- 显示所有自动生成的虚拟列
SHOW VIRTUAL COLUMNS WHERE table='test';
╭────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╮
│ database │ table │ source_column │ virtual_column_id │ virtual_column_name │ virtual_column_type │
│ String │ String │ String │ UInt32 │ String │ String │
├──────────┼────────┼───────────────┼───────────────────┼──────────────────────────┼─────────────────────┤
│ default │ test │ val │ 3000000000 │ ['id'] │ UInt64 │
│ default │ test │ val │ 3000000001 │ ['name'] │ String │
│ default │ test │ val │ 3000000002 │ ['pricings'][0]['price'] │ String │
│ default │ test │ val │ 3000000003 │ ['pricings'][0]['type'] │ String │
│ default │ test │ val │ 3000000004 │ ['pricings'][1]['price'] │ String │
│ default │ test │ val │ 3000000005 │ ['pricings'][1]['type'] │ String │
│ default │ test │ val │ 3000000006 │ ['tags'][0] │ String │
│ default │ test │ val │ 3000000007 │ ['tags'][1] │ String │
╰────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╯
监控命令
| 命令 | 用途 |
|---|---|
SHOW VIRTUAL COLUMNS | 查看自动创建的虚拟列 |
REFRESH VIRTUAL COLUMN | 手动刷新虚拟列 |
FUSE_VIRTUAL_COLUMN | 查看虚拟列元数据 |
性能结果
虚拟列提供:
- 5-10 倍 JSON 字段访问加速
- 自动优化,无需修改查询
- 降低查询处理资源消耗
- 对现有应用透明加速
虚拟列在后台自动工作——只需启用功能,Databend 将优化您的 JSON 查询。

